Chapter 14, “Reproduction,” delves into the fundamental concepts of how organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of species.
This chapter highlights the diverse mechanisms of reproduction, including both asexual and sexual methods, supported by clear explanations, examples, and diagrams.
Our comprehensive notes, structured topic-wise, aim to provide students with concise, easy-to-understand material for exam preparation and in-depth learning.



































Topics Covered in These Notes
The solved notes for Chapter 14 include the following key topics:
- Definition and significance of reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction methods (Binary Fission, Budding, Spore Formation, etc.).
- Sexual reproduction in plants, including pollination, alternation of generations, and seed formation.
- Fertilization and its types (external and internal).
- Differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
- Multiple-choice questions (MCQs), short questions, and long questions.
Class 10 Biology Chapter 14 Solved Notes Topic Wise
1. Asexual Reproduction
Definition: Asexual reproduction involves a single organism producing offspring without the fusion of gametes. It results in genetically identical offspring.
Methods of Asexual Reproduction:
- Binary Fission: Organisms like bacteria and amoeba split into two identical cells.
- Fragmentation: Organisms such as planaria regenerate into new organisms when cut into pieces.
- Budding: Buds grow on organisms like yeast and hydra, eventually detaching to form new individuals.
- Spore Formation: Seen in fungi like Rhizopus, spores develop within sporangia and disperse under favorable conditions.
- Parthenogenesis: Unfertilized eggs develop into new organisms, as seen in certain insects and amphibians.
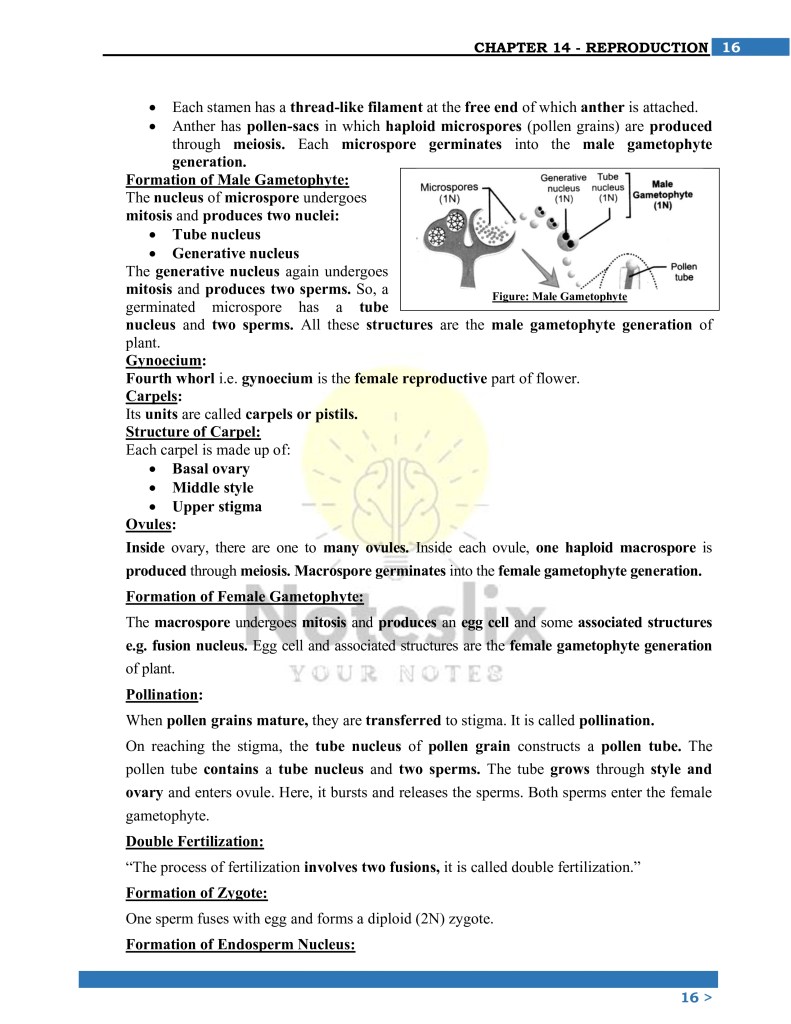
2. Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Definition: This type of reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring with genetic variation.
Key Concepts:
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma.
- Self-pollination: Within the same plant.
- Cross-pollination: Between different plants of the same species.
- Alternation of Generations: Plants alternate between a haploid gametophyte stage and a diploid sporophyte stage.
- Seed Formation: Following fertilization, zygotes develop into seeds, which germinate under favorable conditions.
Tool for Success in Exams
These notes are curated to align with exam requirements. Each topic is simplified for easy understanding and includes well-structured answers. Students can use these notes to:
- Learn accurate definitions and concepts.
- Practice MCQs, short questions, and long questions.
- Review diagrams and flowcharts for visual clarity.
Colored Notes
The solved notes include vibrant illustrations and labeled diagrams, such as:
- Binary fission in amoeba.
- Budding in yeast and hydra.
- Flower structure highlighting pollination pathways. These visuals make learning engaging and help in better retention.
Notes Are Free to Use
These solved notes are available for free, ensuring accessibility for all students. By utilizing these resources, learners can save time and effort while focusing on understanding concepts and improving their academic performance. The free availability ensures that no student is left behind due to a lack of resources.
Notes Are Mistake-Free
The notes have been carefully reviewed and are free of errors. The content aligns with the curriculum, providing accurate and precise information.
Key definitions, examples, and explanations have been verified to avoid confusion and enhance clarity, ensuring students get the best quality material for their studies.
Conclusion
Class 10 Biology Chapter 14, focusing on reproduction, is a critical part of the curriculum. These solved notes offer an invaluable tool for understanding the chapter’s concepts in depth, with well-structured answers, clear diagrams, and comprehensive explanations.
By using these notes, students can effectively prepare for their exams and develop a solid foundation in biology.
Other Class 10 Biology Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 12 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 13 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 15 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 16 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 17 Solved Notes Topic Wise
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 18 Solved Notes Topic Wise

