Direct and indirect speech are essential components of English grammar that play a crucial role in effective communication.
Understanding the nuances of transforming direct speech into indirect speech and vice versa allows individuals to accurately convey spoken messages in written form.
This guide focuses on the rules, transformations, and examples of direct and indirect speech to simplify this concept for 10th-class students.









10th Class English Grammar Direct and Indirect Speech
Topics Covered in These Notes
These notes comprehensively cover the following key areas of direct and indirect speech:
- Definition and differences between direct and indirect speech.
- Basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech.
- Changes in pronouns, verbs, and adverbs during conversion.
- Handling interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences.
- Specific cases such as reporting in the present, past, and future tenses.
Rules for Conversion
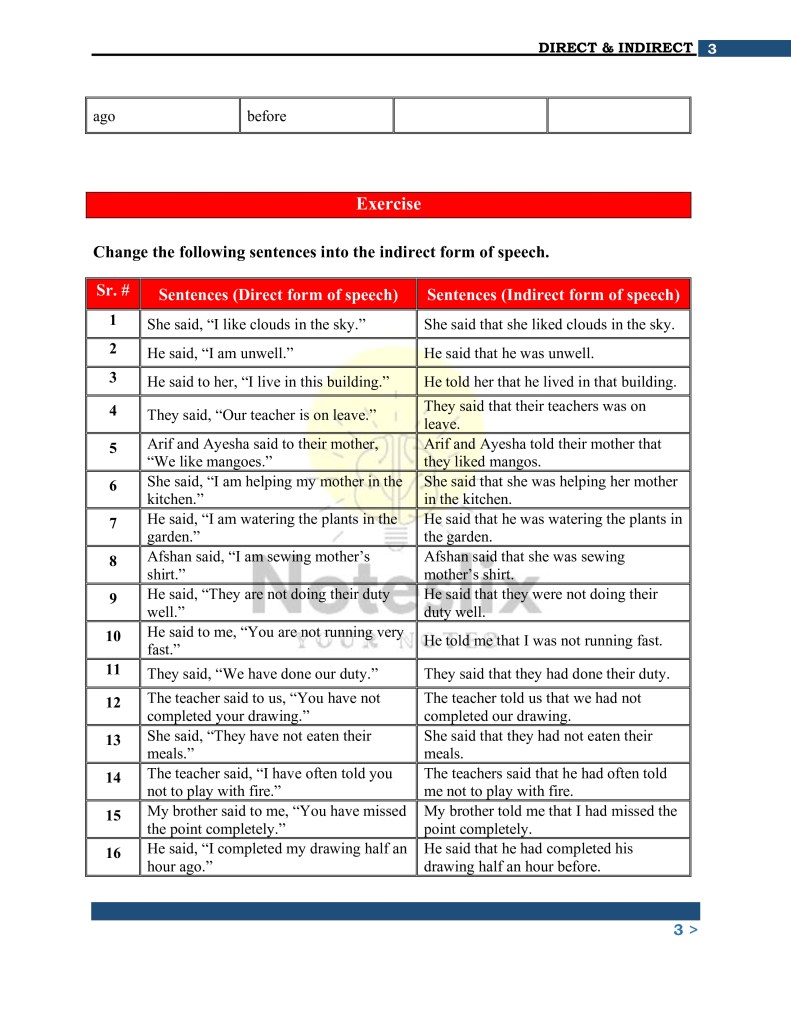
The notes provide clear explanations of essential rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech, such as:
- Tense Changes: Adjusting verb tenses depending on the reporting verb.
- Pronoun Adjustments: Modifying pronouns to maintain grammatical consistency.
- Adverb Changes: Transforming adverbs of time and place to fit the context.
- Conjunction Usage: Introducing conjunctions like “that,” “whether,” or “if” based on sentence type.
For instance:
- Direct: She said, “I am doing my homework.”
- Indirect: She said that she was doing her homework.
Tool for Success in Exams
These notes serve as a comprehensive tool for exam preparation. By following the rules and examples provided, students can confidently,
Tackle any question on direct and indirect speech. The notes simplify complex grammar rules, making it easier to retain and apply them during exams.
Colored Notes
To enhance readability, these notes feature colored highlights for important rules, examples, and tips. This approach helps students quickly identify and focus on key points, improving their study efficiency and retention.
Notes Are Free to Use
These notes are freely available for students to use as a reliable resource for learning direct and indirect speech. The structured format and detailed examples make them an invaluable tool for both classroom learning and self-study.
Notes Are Mistake-Free
Compiled with utmost care, these notes have been thoroughly reviewed to ensure accuracy and clarity. Every example and rule has been verified, making them a dependable resource for students aiming to master direct and indirect speech.
Practical Examples
Here are some practical examples to illustrate the application of the rules:
- Statement Conversion:
- Direct: He said, “I will help you tomorrow.”
- Indirect: He said that he would help me the next day.
- Question Conversion:
- Direct: She asked, “Where are you going?”
- Indirect: She asked where I was going.
- Imperative Conversion:
- Direct: The teacher said, “Complete your homework.”
- Indirect: The teacher instructed them to complete their homework.
Conclusion
Mastering direct and indirect speech is vital for clear and effective communication. These notes provide a well-rounded understanding of the topic,
Ensuring students can confidently apply these grammar rules in exams and everyday communication. Utilize these resources to strengthen your grammar skills and excel in your studies.

